
Childhood Lead Exposure

23 States exceed 5ug/dL limit CSIR-NITI Aayog report-Lead.

| State | Value |
|---|---|
| Bihar | 10.42 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 8.67 |
| Madhya Pradesh | 8.32 |
| Jharkhand | 8.15 |
| Chhattisgarh | 7.46 |
| Andhra Pradesh | 7.14 |
| Odisha | 6.94 |
| Assam | 6.72 |
| Karnataka | 6.62 |
| Telangana | 6.61 |
| Tripura | 6.55 |
| Tamil Nadu | 6.23 |
| Meghalaya | 6.00 |
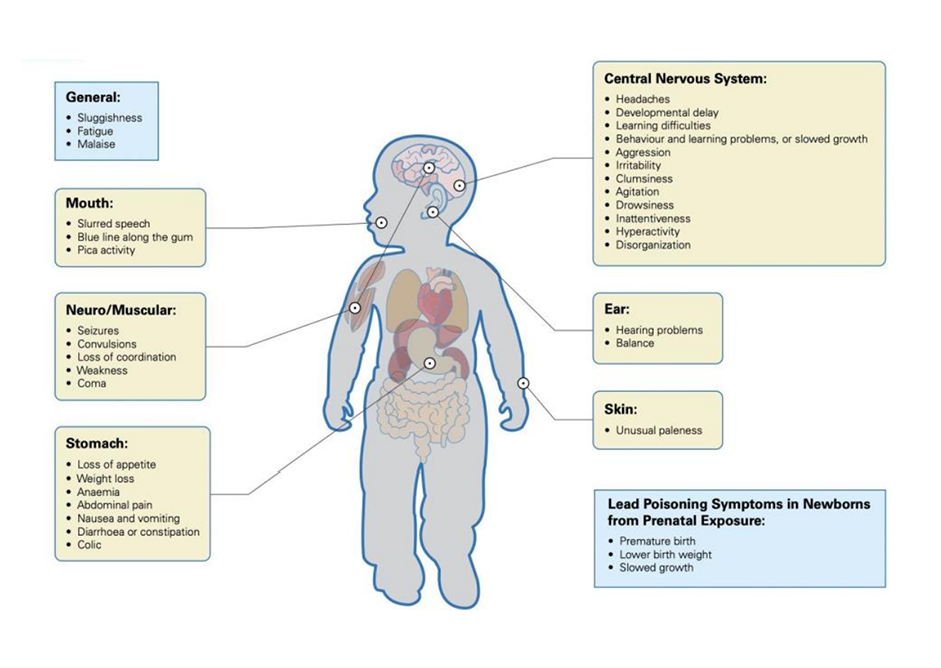
Health impacts of Lead Exposure
Major Source of Lead Exposur in India
NO LONGER GASOLINE
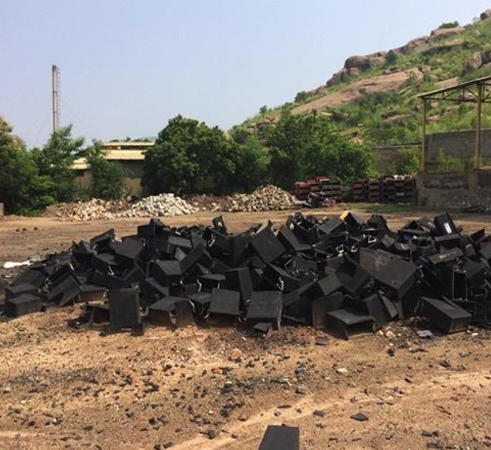

Substandard Informal Battery Recycling
Non-complian t Formal Recyclers
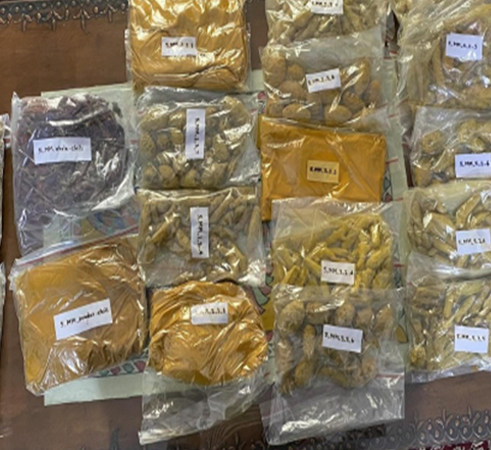

Adulterated Spices
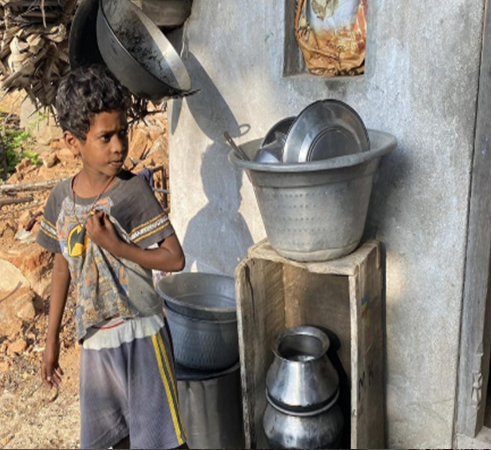

Cookware (Metallic alloys & Glazed Ceramics)
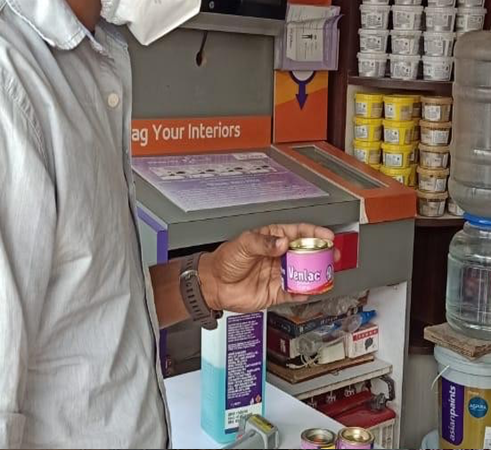

Local Paint

Cosmetics (Kumkum)
Finding of The BLL Survey in Bihar
2021 study in Patna
- 135 kids tested & their houses assessed in Patna.
- 87% kids with BLLs ≥5 µg/dl.
- The average BLL 14.9 µg/dL, 3 times the WHO limits
- Adulterated spices, local paint & lead in dust identified as the key sources.
2023 study
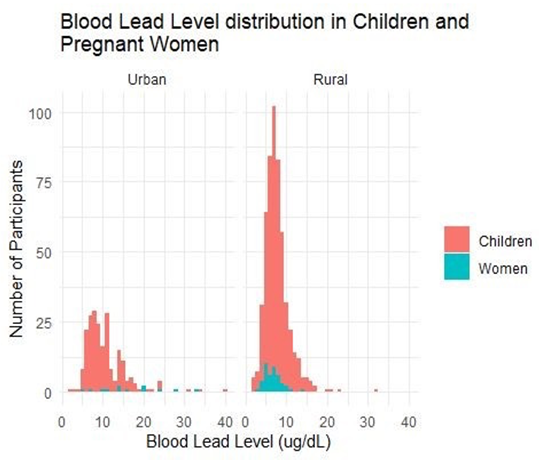
- 699 children and 55 pregnant women tested for BLL in 8 districts.
- More than 90% of Children in urban & 80% of children in rural areas were found with BLL above 5 µg/dL
- Average BLL in kids = 8 µg/dL
- Average BLL in pregnant women = 7.8 µg/dL

First Lead Source Apportionment Study: Bihar
- 80% of households spices found with >10 ppm of lead concentration.
- Median concentration in turmeric was found 145 ppm, with a maximum upto 5,000 ppm
- Elevated levels of lead were also found in chili and coriander powder
- These results prompted deeper investigation into lead in spices across North India with Stanford University
- 20 cities across Bihar, Eastern part of Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal and Jharkhand
- Turmeric, chili and coriander samples collected from markets and analyzed
- Results forthcoming
Solvable Problem
- Solvable at modest cost as tested solutions exist
- Monitoring programs - Test blood in newborns, schoolkids.
- Source analysis - Where is the lead.
- Interventions related to sources.
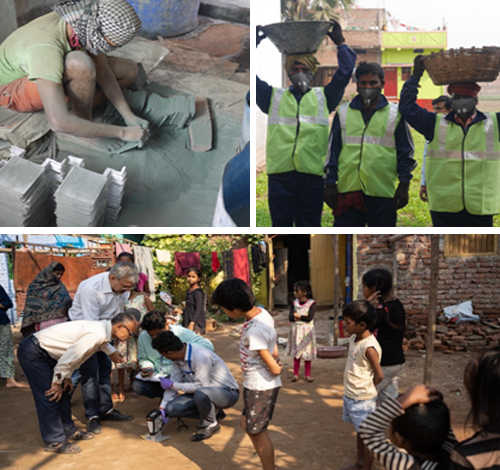


Reducing Lead Poisoning Among Children in Karmalichak, Bihar, India (2016-19)
Issue: Through the Toxic Site Identification Program in 2016, an informal battery-plates manufacturer was identified operating for 2 decades at substandard level from a residential area in Karmalichak. The soil-assessment showed high levels of Lead all around. Blood lead levels (BLL) testing among 40 school kids revealed very high BLL impacting their Intellectual capacity and brain development.
Solution: A risk reduction project was implemented with soil capping of contaminated outdoor areas followed by home and school-cleanups & community education
Impact:
- This first lead risk reduction project lead to the first lead source apportionment study in India
- The State Pollution Control Board took action & shutdown the unit
- Lead in soils restored to the safe level (below 400 ppm)
- Increased awareness and stakeholder participation

